- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- 23 Oct 2023
T1 Evidence in Adults

Prescribing Information Toujeo (insulin glargine 300 units/mL)
Prescribing Information Lantus (insulin glargine 100 units/mL)
.jpg)
Ask us your questions about our products, patient materials or organising a meeting.
Toujeo® can support your patients with T1DM
Discover the Toujeo® Evidence in T1DM below and get access to patient supporting tools and materials for your T1 patients who have been prescribed Toujeo®.
PK/PD
Toujeo® is associated with a more stable and prolonged activity profile over a full 24-hour period than insulin glargine 100 units/mL1
Toujeo® is associated with a flatter PK/PD profile vs insulin degludec 100 units/mL2
.jpg)
Toujeo® has a flatter, more stable activity profile – extending beyond 24 hours with a flexible dosing window (+/- 3 hours).
- PK/PD study in people with T1DM using euglycaemic-clamp technique at steady state. The results of euglycaemic clamp studies do not necessarily predict clinical outcomes in all patients.
.jpg)
Compared with insulin degludec, Toujeo® at a clinically relevant dose (0.4 units/kg/day) provides a more stable and evenly distributed PK/PD profile with less within-day fluctuation in adults with T1DM.1 Toujeo® also had a 20% lower (p=0.047) within-day variability of the smoothed GIR curve vs insulin degludec.1
- For GIR data a smoothing factor (LOESS factor 0.15) was applied. PK/PD study in people with T1DM using euglycaemic-clamo technique. The results of euglycaemic clamp studies do not necessarily predict clinical outcomes in all patients.
- The within-day variability of the smoother GIR curve was similiar between Toujeo® 0.6 units/kg/day and insulin degludec 0.6 units/kg/day. Both insulins provided exposure and acctivity until 30 hours (end of clamp).
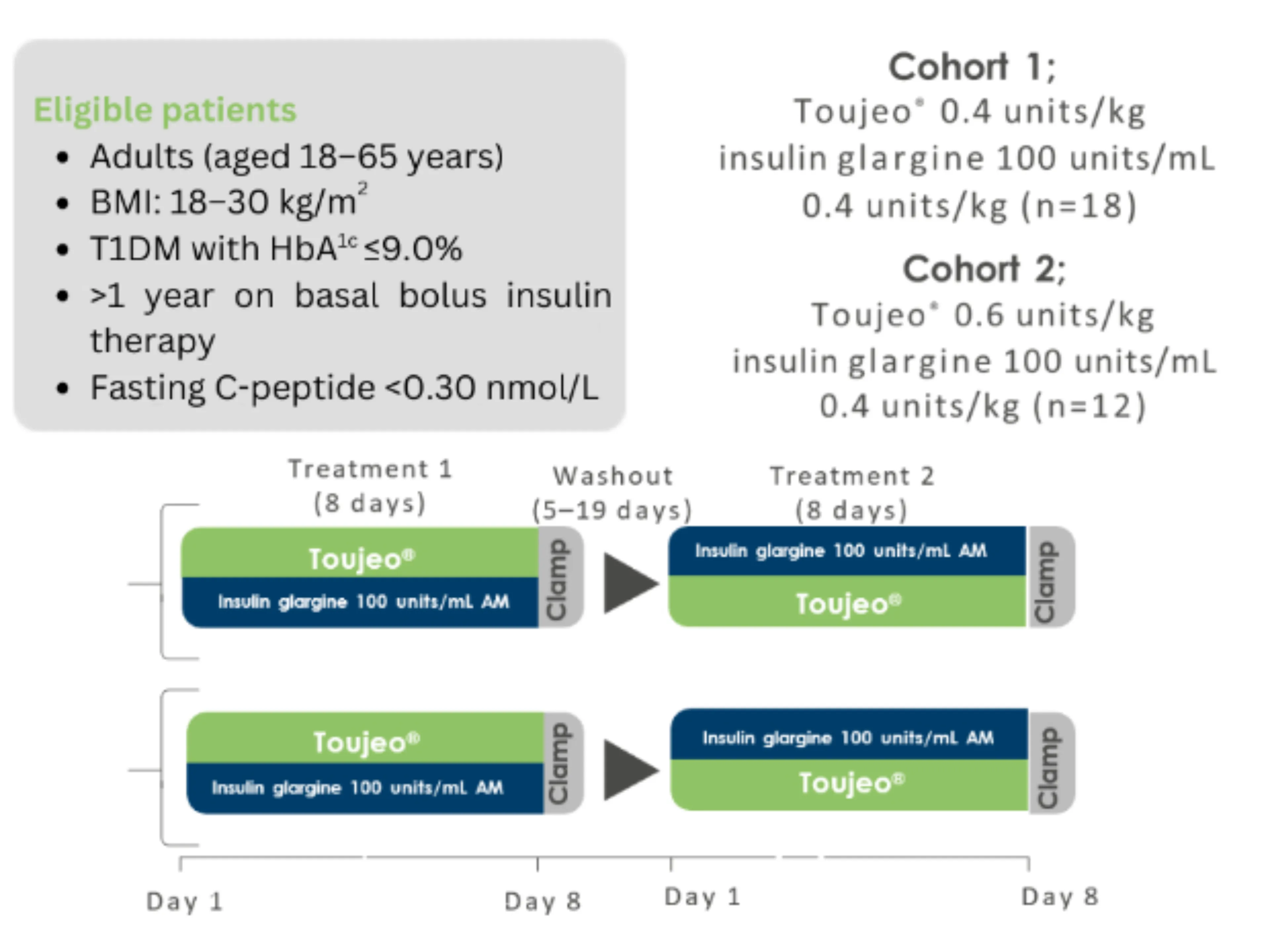
Study design: Becker RHA, et al. 2015.1
Study aim: to characterise the PK/PD of Toujeo® compared with insulin glargine 100 units/mL at steady state in people with T1DM.
Study design: Single-centre, randomised, double-blind, two-treatment, two-period, two sequence crossover euglycaemic clamp study.
Primary endpoint: GIR and INS profiles in steady state.
Treatment during the washout period was unchanged from that recieved prior to the study. For GIR and BG data a smoothing factor (LOESS factor 0.15) was applied.
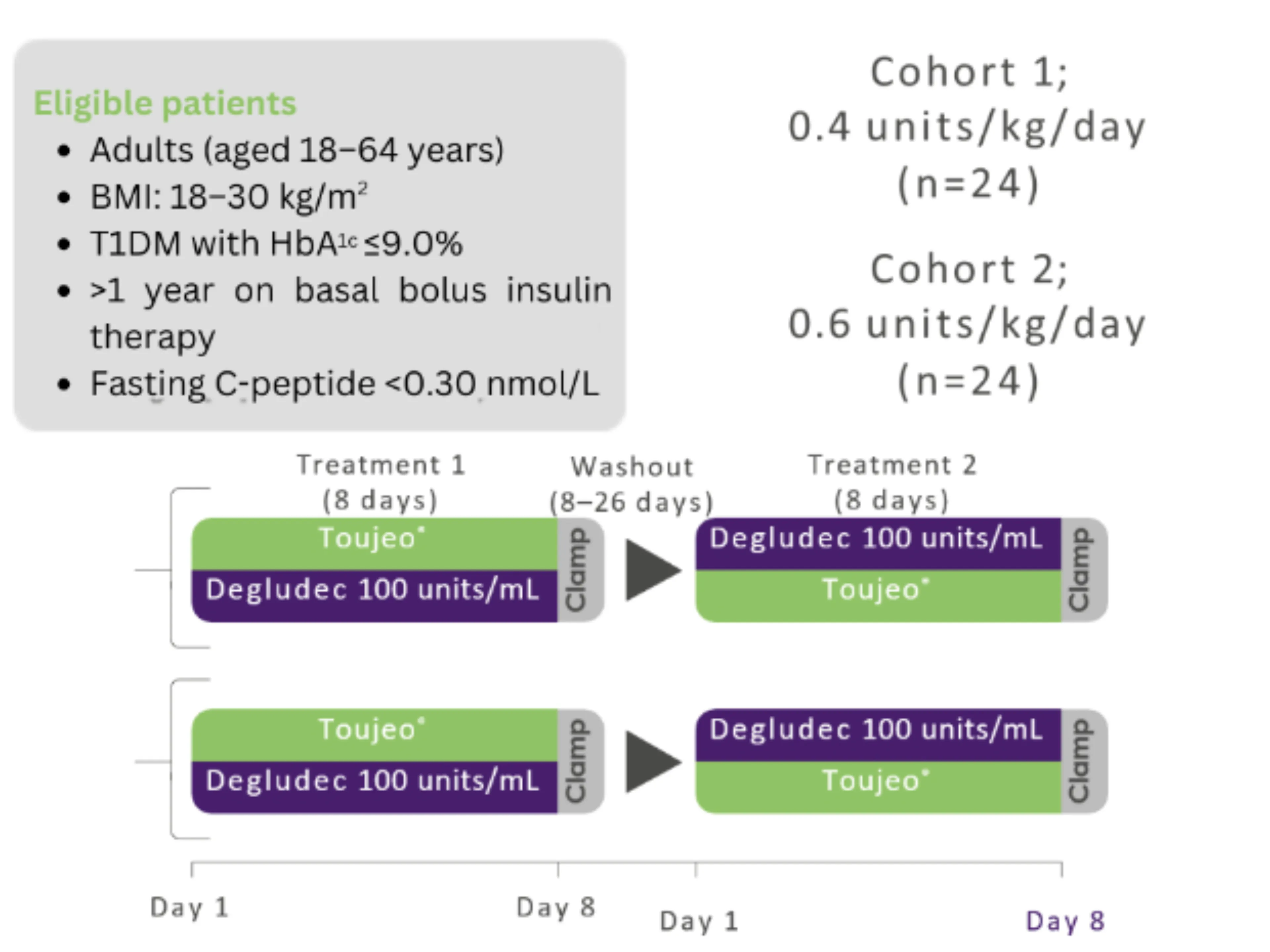
Study design: Bailey TS, et al. 2018.2
Study aim: to compare the PK/PD properties of 0.4 and 0.6 units/kg/day Toujeo® with insulin degludec 100 units/mL in people with T1DM
Study design: Single-centre, randomised, double-blind, two-treatment, two-period, two-sequence crossover euglycaemic clamp study
Primary endpoint: Fluctuation (within-day variability) of the smoothed GIR curve over a 24-hour dosing period in steady state (GIR-smFL0-24)*
Treatment during the washout period was unchanged from that recieved prior to the study. For GIR and BG data a smoothing factor (LOESS factor 0.15) was applied.
*The area of the individual smoothed GIR above and below the individual average GIR line is calculated, providing the mean amplitude of GIR fluctuations around the average GIR over 24 hours.
The clinical implications of PK/PD data require further evaluation including CGM and larger clinical studies. PK/PD study in people with T1DM using euglycaemic-clamp technique at steady state. The results of euglycaemic clamp studies do not necessarily predict clinical outcomes in all patients.
CGM
Toujeo® vs Insulin Glargine 100 U/mL3
.jpg)
.jpg)
Meta Analysis
Toujeo® vs Insulin Glargine 100 U/mL4
Post-hoc meta-analysis of three EDITION 6-month, Phase III, randomised clinical trials
Post-hoc meta-analysis aim: Exploring the risk for severe hypoglycaemia with Toujeo® vs insulin glargine 100 units/mL in the pool of studied patients with T1DM.

Edition 4 (549 adults), Edition Junior (463 children), Edition JP 1 (243 adults).
Real World Evidence: Sparta
Toujeo® vs other basal insulins5
A multicentre, UK, retrospective, observational study to assess the effectiveness of Toujeo® in treating people with Type 1 diabetes mellitus in routine clinical practice (SPARTA).
Primary endpoint: Change in HbA1c levels from baseline to Month 6 after Toujeo® initiation.

298 patients with T1DM were recruited.
Toujeo
Toujeo® is indicated as treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children from the age of 6 years.
CI, confidence interval; CGM, continuous glucose monitoring; GIR, glucose infusion rate; LOESS, locally weighted scatter plot smoother; PD, pharmacodynamic; PK, pharmacokinetic; SC, subcutaneous; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; HbA1c, glycated haemoglobin; LS, leastquare; NS, not significant; AE, adverse event; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
References
- Becker R et al. Diabetes Care 2015;38:637-643
- Bailey TS, et al. Diabetes Metab. 2018;44:15-21
- Bergenstal RM, et al. Diabetes Care 2017;40:554-560.
- Danne T, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22:1880-5.
- Pang T, et al. Diabetic Medicine October 2018
- Battelino T, et al. Diabetes Ther 2020;11:1017-1027
MAT-XU-2205634 (v6.0) Date of Preparation: October 2023